

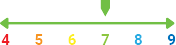



The soil temperature should exceed 12 °C at drilling
The nutrient demand is similar to that of maize.
Sorghum originates from Africa and has similar requirements to maize, but with a very low water demand and high heat tolerance. The dense and deep root system efficiently extracts water and nutrients from the soil and the plants are capable of regenerating after severe drought stress and wilt.
The field should be free of weeds, due to the relatively slow development of young plants. The required soil temperature of 12 to 14 °C is reached relatively late in the year.
(Unit/t of production)
(Unit/t of production)
N
4.1
4,1
Sensitive
P₂O₅
1,8
1,8
Sensitive
K₂O
4,8
4,8
Sensitive
MgO
0,4
0,4
Moderately Sensitive
TE
The required nutrients can be applied before planting, however, nitrogen fertilization of more than 100 kg per hectare needs to be split. A potassium rich NPK fertilizer usually covers the supply of the main nutrients. The remaining nitrogen should be applied up to four-leaf growth stage.
A NP-fertilizer placed near the roots, accelerates the early development. Organic fertilizers must be incorporated into to soil in order to avoid nitrogen volatilization.
First application

Second application

The entire nutrient demand can be supplied using an appropriate NPK formulation. Nitrogen fertilization exceeding 100 kg/ha should be split into two applications. The fertilization is based on offtake and supply from the soil. The high potassium demand can be covered partially by organic fertilizers.
The second application supplements nitrogen if the demand exceeds 100 kg/ha. Splitting of the nitrogen fertilization is particularly recommended on light soils. The N top dressing should not exceed the four-leaf growth stage.
LAT Nitrogen Austria GmbH
St.-Peter-Strasse 25
4021 Linz, Austria




