
Phosphorus
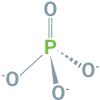
(P)
1. Nutrients contained in organic matter of all types, including livestock effluent, crop residue and other organic by-products of human activities, are an important resource for fertilization.
2. Phosphate rock is extracted from open-cast mines and is processed using acids to produce more soluble forms that can be assimilated by plants.
3. Mineralisation of organic matter in the soil releases soluble mineral phosphorus (phosphate).
4. Phosphorus is continuously changing between fixed, adsorbed and soluble forms.
5. The leaching of soluble phosphorus (removal to deeper layers of soil by water) is not ver common.
6. Not much phosphorus is carried away outside the field; it may happen due to runoff and erosion (phosphorus linked to solid particles).
7. Plant roots only absorb phosphorus from the soil solution.
8. The harvest is used as food (for humans or livestock), which is the fundamental objective of farming.
Very
Fairly
Moderately
| P | P₂O₅ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Potatoes | |||
| Winter Rapeseed | |||
| Silage Maize | |||
| Grain Maize | |||
| Sugar Beet | |||
| Sunflower | |||
| Carrot | |||
| Spring Barley | |||
| Tomato | |||
| Cabbage | |||
| Cucumber | |||
| Fiber Flax | |||
| Winter Wheat | |||
| Winter Barley | |||
| Apple | |||
| Cherries | |||
| Grape Vine | |||
| Lettuce | |||
| Pear | |||
| Strawberry |
Phosphorus-deficient plants show purple and reddish coloration on young leaves, and on sheaths.
In the soil, it can block the availability of zinc. It may lead to eutrophication due to runoff into water courses.
LAT Nitrogen Austria GmbH
St.-Peter-Strasse 25
4021 Linz, Austria